Every year, diabetes continues to progress and affects several million people. The monitoring program developed by Public Health France aims to provide indicators of the frequency, severity and evolution of diabetes in France. These data are made available annually. On the occasion of the world diabetes dayPublic Health France publishes updated diabetes surveillance data in 2020, also available on its Geodes platform (prevalence, complications, follow-up frequency of recommended examinations). A new indicator on the incidence of type 1 diabetes in children is available at the regional level up to 2017.
Diabetes in France: key figures and results in 2020
A disease still on the rise
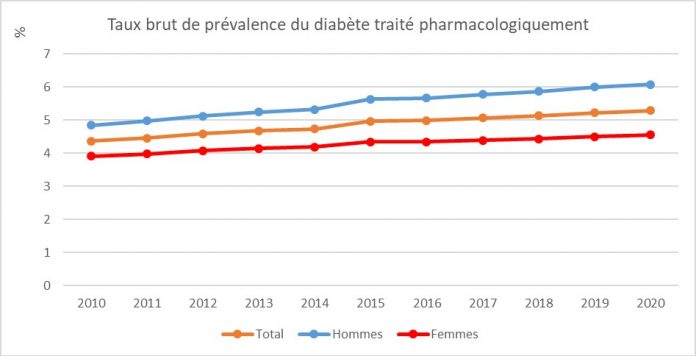
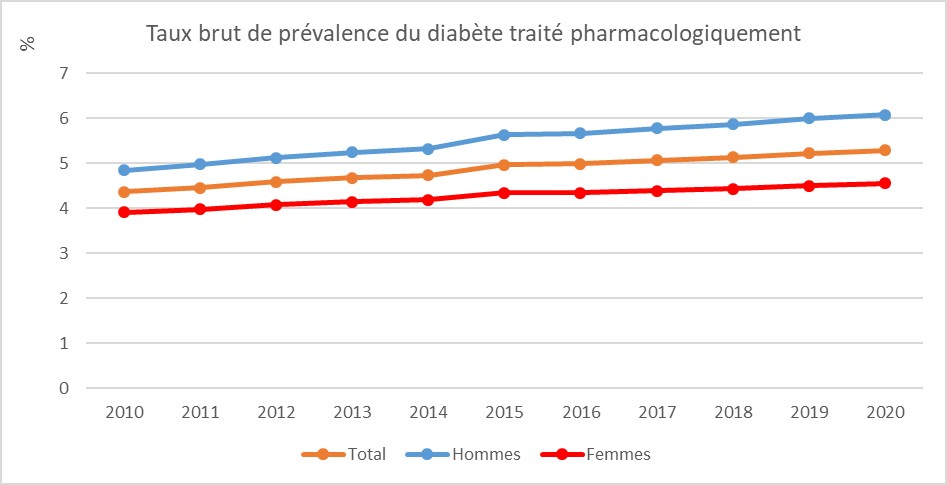
In 2020, the diabetes continued to grow with almost the same level of growth as in previous years.
Who is most affected by diabetes?
Diabetes is more common in men than in women, with the exception of overseas territories where women are the most affected.
What is the percentage of diabetics treated with medication in France?
In France in 2020, more than 3.5 million people are treated by medication for diabetes, i.e. 5.3% of the population.
Territorial disparities remain very marked with a much higher frequency of diabetes in the overseas departments and in Seine Saint-Denis. There is also a high frequency in the departments of Val d’Oise and North-East of the metropolis. On the other hand, the departments located to the west of the metropolis and in particular in Brittany record the lowest frequencies.
Diabetes-related complications: fewer hospitalizations for foot ulcers and strokes
Complications related to diabetes remain frequent and stable but a slight decrease appears for the 1time times on hospitalizations for foot ulcers and stroke
In 2020, chronic complications related to diabetes remain very frequent. However, for the first time since monitoring began in 2010, hospitalizations for foot ulcers and stroke have decreased, but only moderately. The occurrence of lower limb amputations, transmural myocardial infarctions and end-stage chronic renal failure, which had been relatively stable since the start of follow-up, also decreased, but only modestly.

Learn more about the standardized incidence rates of diabetes-related complications on Géodes
Diabetes monitoring: the frequency of recommended examinations is slightly down
Clinical monitoring of people with diabetes is guided by recommendations for care pathways established by the Haute Autorité de Santé. Until 2019, the follow-up frequency of the recommended examinations increased each year. In 2020, the follow-up of all examinations decreased, but in a modest way. The largest decreases concern the 3 HbA1c assays (marker of glycemic balance), and dental consultations which fell respectively, by -3.4 and -4.2 points between 2019 and 2020.

In a context where the use of healthcare has fallen sharply in the general population, due to the COVID-19 health crisis, the decrease in the use of the 3 recommended HbA1c assays remains moderate. Nevertheless, it is necessary to remember that only 52% of people with diabetes have benefited from it, even though it is an essential indicator for monitoring glycemic balance and therefore for preventing diabetes complications.
Type 1 diabetes in children: an increase of about 4% per year
The occurrence of type 1 diabetes in children is increasing by about 4% per year : the national incidence rate is 18.0 per 100,000 in 2013-2015 and 19.5 per 100,000 over the period 2015-2017.
Regional variations are observed, with the highest incidence rates in Martinique, Occitanie and Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur and the lowest incidence rates in Guyana, Guadeloupe and La Réunion – and in France metropolitan area, in the Pays de la Loire, in Normandy and in New Aquitaine.
Diabetes: what you need to know
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic condition characterized by chronic hyperglycaemia (too high blood sugar) linked to a deficiency in the secretion or action of insulin, or both.
There are two main forms of diabetes:
- the type 1 diabetes occurs mainly in children or young adults (about 6% of diabetes cases);
- the Type 2 diabeteswhich is the most common form (more than 90%), occurs mainly in adults but can also appear in adolescence.
There are other forms of diabetes, such as gestational diabetes (which occurs during pregnancy and disappears after childbirth), or cases of diabetes resulting from specific or genetic conditions.
As diabetes progresses, it can lead to serious complications affecting the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys and nerves. However, good control of the disease can significantly reduce the risk of complications.